From Plate to Pulse: Your Guide to a Triglycerides Diet Plan

Last updated on April 3rd, 2025 at 09:29 pm
A triglyceride diet plan is designed to help manage and lower elevated triglyceride levels in the blood, which are linked to cardiovascular risk. From what I've learned, dietary changes shouldn't wait until early signs appear; instead, it’s best to start making necessary adjustments as soon as possible.
The main focus is on cutting back on trans fats and saturated fats—things you find in red meat, full-fat dairy, and processed foods. At the same time, it’s about adding in healthier fats, like those from olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
Increasing fiber from grains, fruits, and vegetables seems to help a lot, especially soluble fiber and Omega-3s, which are known to reduce triglycerides.
Cutting down on sugar, refined carbs [1], controlling portion sizes, and drinking less alcohol are also important.
Plus, choosing lean proteins, staying hydrated, and getting regular aerobic exercise are all part of a good plan to lower triglycerides.
Why You Should Take the Triglycerides Diet Plan
In the big picture of our health, triglycerides play an important role as a measure of the fats circulating in our bloodstream. Elevated levels are often linked to a higher risk of cardiovascular issues [2], which is why managing them is so important for overall well-being.
The triglycerides diet plan is a straightforward, science-backed approach designed to help regulate these fats while promoting heart health. When I looked at the details of this diet, I discovered that it’s not just about following the rules—it’s really more of a guide to better cardiovascular wellness.
From the omega-3s in fatty fish to the antioxidants in colorful fruits and veggies, this plan isn’t about restricting yourself—it’s about building a lifestyle that supports and protects your heart. It’s definitely worth considering when looking for a practical way to boost heart health and resilience.
Foods for a Triglycerides Diet Plan
Here are some food options that I’ve identified for a triglycerides diet plan to fight the risk of cardiovascular problems such as heart attacks and strokes. Foods with the right nutrients, such as fatty acids and soluble fiber.
1. Fatty Fish
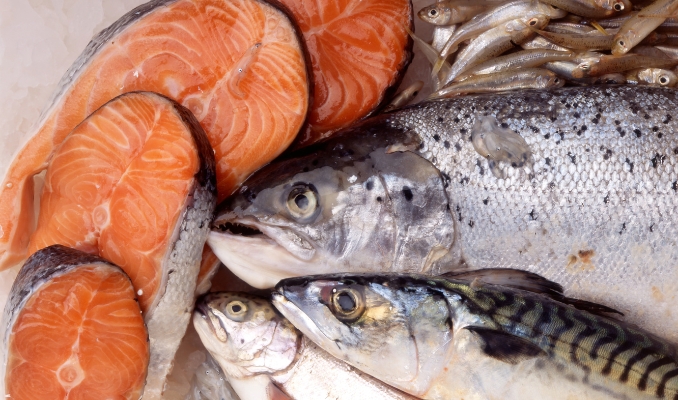

Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are great sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
From what I’ve gathered, omega-3s have some serious benefits, especially when it comes to lowering triglyceride levels by reducing their production in the liver.
They also help with heart health by improving lipid profiles, reducing inflammation, and supporting overall cardiovascular function.
- Salmon – Salmon is beneficial for a triglycerides diet plan due to its rich omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) and DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid).
- Mackerel – Similar to Salmon, Mackerel has fatty acids that can lower the risk of arrhythmias and enhance blood vessel function.
- Sardines – Regular consumption of sardines has been associated with lowering heart disease risk factors.
- Trout – Trout is a nutritious and heart-healthy choice that can be beneficial for a diet to lower triglycerides. It is also a good source of lean protein, which is important for immune function, muscle maintenance, and overall health.
- Herring – Herring is a nutrient-dense food, providing essential nutrients such as vitamin D, vitamin B12, selenium, and unsaturated fats.
These nutrients contribute to bone health, immune function, and overall well-being.
2. Healthy Oils

Healthy oils are an important part of a triglycerides diet plan because they provide beneficial fats. These fats—monounsaturated and polyunsaturated —can have a positive effect on triglyceride levels and overall heart health.
- Olive Oil – Olive oil mainly consists of monounsaturated fats, with oleic acid as the primary fatty acid.This type of vegetable oil is considered heart-healthy. It has been linked with improved lipid profiles, including lower triglyceride levels.
- Canola Oil – Canola oil is low in saturated fat, making it a heart-healthy alternative to oils high in saturated and trans fats. Diets low in saturated fat are generally recommended for managing triglyceride levels.
- Flaxseed Oil – Flaxseed oil is one of the richest plant-based sources of ALA, a type of omega-3 fatty acid.
- Omega-3s, including ALA, have been associated with cardiovascular benefits, including the potential to lower triglyceride levels.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are essential for a triglycerides diet plan due to their nutrient-rich profile, including healthy fats, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals.
They are also rich in polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats, including omega-3 fatty acids.
- Almonds – Almonds are a significant source of oleic fatty acid. These healthy fats have been associated with favorable effects on lipid profiles, including a reduction in triglyceride levels.
- Walnuts – Walnuts are among the rare plant-based sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid.
- Hazelnuts – The monounsaturated fats in hazelnuts regulate lipid metabolism, contributing to lower triglyceride levels and improved overall lipid balance.
4. Whole Grains

Whole grains such as quinoa, oats, whole wheat, and brown rice are packed with dietary fiber, especially soluble fiber.
Soluble fiber can help lower triglyceride levels by slowing down how sugars and fats are absorbed, which in turn helps improve overall lipid balance.
- Oats – Oats contain a significant amount of soluble fiber, specifically beta-glucans. Soluble fiber has been shown to have a cholesterol-lowering effect, including the reduction of triglyceride levels.
- Barley – The soluble fiber in barley helps lower triglyceride levels by slowing the absorption of dietary fats and sugars, regulating lipid metabolism, and promoting the excretion of bile acids.
- Quinoa – Quinoa is a complete protein source, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. Including high-quality protein in the diet can support muscle maintenance, metabolism, and overall health.
- Brown Rice – Brown rice is a good source of dietary fiber, including both soluble and insoluble fiber. The soluble fiber content is particularly important for managing triglyceride levels.
- Whole Wheat Products – Regular consumption of whole wheat has been associated with progress in lipid profiles, including a reduction in triglycerides and an increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL or “good” cholesterol).
5. Fruits

Many fruits, such as apples, berries, and citrus, are rich in soluble fiber. Soluble fiber helps lower triglyceride levels by slowing down the absorption of sugars and fats, promoting better lipid metabolism.
- Berries – Berries are essential for a triglycerides diet plan due to their rich nutrient content, particularly fiber, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds that contribute to cardiovascular health.
- Citrus – Citrus fruits, such as limes, lemons, and oranges, are excellent sources of vitamin C. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, contributing to heart health.
- Apples – Apples are essential for a diet to lower triglycerides due to their nutritional composition, which includes fiber, antioxidants, and various health-promoting compounds.
- Avocados – Avocados are a rich source of monounsaturated fats, specifically oleic acid. These healthy fats have been associated with favorable lipid profile effects, including reduced triglyceride levels.
6. Vegetables

Vegetables are essential for a triglycerides diet plan due to their nutrient-rich composition, including fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
Leafy green vegetables like spinach, peppers, broccoli, and kale are excellent sources of dietary fiber and healthy daily calories.
- Spinach – Spinach is a good source of soluble fiber, particularly pectin.
- Broccoli – Broccoli is low in calories but high in essential nutrients, making it a great choice for those aiming for weight management.
- Cauliflower – A vegetable low in carbohydrates and calories, making it a significant choice for those focusing on weight management and managing triglyceride levels.
- Brussels sprouts – Brussels sprouts are low-fat vegetables that contain antioxidants, including vitamin C and vitamin K. These antioxidants help protect the cells from oxidative stress, supporting heart health.
7. Legumes

Legumes are a great source of soluble fiber and are naturally low in fat.
This aids in reducing triglyceride levels by slowing the absorption of fats and sugars, making them a protein source that supports heart health.
- Beans – Beans, including black beans, kidney beans, and chickpeas, are high in soluble fiber.
- Soluble fiber helps lower triglyceride levels by slowing down the absorption of fats and sugars, promoting overall lipid balance.
- Peas – Fresh or frozen, peas are a good source of soluble fiber.
- Lentils – Lentils are high in soluble fiber, particularly beta-glucans.
8. Dairy

Dairy products like cheese, yogurt, and milk are solid sources of protein. Fat-free options, in particular, offer the benefits of protein without the extra fat, which is great for overall nutrition.
Plus, they can help keep you feeling full, which supports weight management.
- Low-Fat Yogurt – This yogurt is a good source of protein, an essential nutrient that supports overall nutrition. Including adequate protein in the diet promotes satiety and aids in weight management.
- Skim Milk – Skim milk is virtually devoid of saturated and trans fat, which is linked to elevated triglyceride levels. Choosing this low-fat milk helps manage saturated fat intake, supporting heart health and lipid balance.
- Reduced-Fat Cheese – Reduced-fat cheese contains less saturated fats compared to full-fat varieties. High fat intake is linked to elevated triglyceride levels, so choosing reduced-fat options aligns with heart-healthy recommendations.
9. Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices add robust flavors to dishes without excessive salt, sugar, or unhealthy fats. This benefits those managing their triglyceride levels, as it creates tasty meals without compromising health.
- Garlic – Studies suggest that garlic may have a modest impact on lipid levels, including triglycerides. Allicin, a sulfur-containing compound in garlic, is significant in these potential lipid-lowering effects.
- Ginger – Ginger contains bioactive compounds with potent anti-inflammatory effects. Chronic inflammation is associated with various cardiovascular issues, including elevated triglyceride levels. Ginger's anti-inflammatory properties contribute to overall heart health.
- Turmeric – Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Cinnamon – Research has explored cinnamon's potential to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels. Cinnamon is a low-calorie spice, making it an ideal choice for flavoring meals without contributing extra calories. This supports weight management, which is crucial for controlling triglyceride levels.
Key Dietary Guidelines
As I go through the essential dietary guidelines that can support following the triglycerides diet plan for improved fitness and well-being. I get to understand that rather than imposing strict limitations, it is focused on making choices that meet the body’s needs.
The guidelines address aspects like portion sizes and meal frequency. While following them isn’t mandatory, doing so can help you gain the greatest benefits from the diet plan.
1. Portion Control

Portion control plays a big role in managing how much you eat, which can directly impact your weight and triglyceride levels. Keeping portions in check also helps stabilize blood sugar and makes your body more sensitive to insulin, lowering the risk of insulin resistance.
By being mindful of portion sizes, it’s easier to avoid overloading on foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats, helping to keep a good balance of nutrients. It’s not just about the physical benefits—portion control also encourages mindful eating, so you can better tune in when you’re hungry or full.
2. Hydration
Drinking enough water is a big part of the triglycerides diet plan. It does a lot for your heart health. It helps keep the blood flowing smoothly, which is important for controlling triglyceride levels.
Water plays a key role in how the liver processes triglycerides and keeps kidneys working well to eliminate waste. Staying hydrated helps with many things, such as knowing when you're hungry or thirsty can prevent unnecessary snacking.
It ensures the proper functioning of the kidneys, aiding in eliminating waste products from the body.
3. Regular Physical Activity

As I follow the triglycerides diet plan, I experienced and proven that regular physical activity plays a big part for the overall health, especially for the heart. Exercise helps manage weight, which is very important for keeping the blood triglyceride levels [3] in a healthy range.
During working out, the body uses insulin better, helping control blood sugar and lowering triglycerides. Exercise also breaks down triglycerides for energy and reduces bad LDL cholesterol in the body.
Additionally, being active helps shrink belly fat and keeps the blood flowing smoothly. Besides these health benefits, moving around is a natural way to relieve stress, making it feel better overall.
I understand the value of incorporating regular exercise into my routine as part of the triglycerides diet plan. By staying active, I can take charge of my health and improve my heart's well-being, one step at a time.
4. Regular Meal Timing
Having my meals at regular times is an essential component of the triglycerides diet plan. I have learned that spacing out my meals throughout the day will help keep my blood sugar levels stable, thus avoiding sudden spikes or drops that can negatively impact my triglyceride levels.
This routine promotes better insulin sensitivity, allowing my body to handle glucose more effectively by storing triglycerides in fat cells properly. Keeping a regular meal schedule helps prevent overeating, supporting weight management and maintaining steady energy levels.
As I understand the value of establishing a regular eating pattern as part of the triglycerides diet plan. Eating meals at regular times throughout the day, I can more effectively manage my blood sugar and triglyceride levels, while also promoting my overall health and well-being.
5. Stress Management

Managing stress is a big part of the triglycerides diet plan, and it does a lot for your heart and triglyceride levels. When stress sticks around, it can boost cortisol levels, potentially making your body produce more triglycerides.
Stress is also linked to emotional eating, bad food choices, and habits like smoking or drinking too much—all things that can mess with your triglycerides. So, taking charge of stress means you're more likely to eat mindfully, cope with challenges in healthier ways, and sleep better.
Conclusion
The guidelines may be beneficial, but it is always important to remember that individual responses to dietary changes can vary. These tips can be helpful for many people, but everyone reacts differently toward their daily diet to lower their triglyceride levels.
It's best to talk to a healthcare professional or a nutrition expert for advice that fits your specific health needs. If you're thinking about following a daily diet to lower your risk of heart disease, getting personalized guidance is important.
A healthcare professional can assess your health, consider any issues you might have, and give you advice that's just right for you. This way, any changes you make to your eating habits are not only effective but also safe and doable over time.
It’s never too late to get a healthy heart! The 14-Day Heart Health Quick Start Program shows you how to naturally improve your cardiovascular system. Check out now!
Rick Kaselj MS, is a leading kinesiologist and injury specialist as well as co-creator of the best-selling Unlock Your Hip Flexors program. Rick creates exercise programs that help people heal injuries and eliminate pain, so they can go back to living a full, active, healthy life.





